Snoring - Sleep Apnea Surgery
Snoring - Sleep Apnea Surgery
Snoring and sleep apnea are breathing problems during sleep, usually caused by upper airway problems. Snoring is the audible breathing that occurs due to the vibration of soft tissues, while sleep apnea involves repeated pauses in breathing. Snoring and sleep apnea surgery usually aims to correct anatomical problems in the nose, throat or mouth. These surgical interventions can include procedures such as adenoid surgery, upper palate and tonsillectomy, base of tongue surgery and adenoid surgery. Surgery is determined depending on the patient’s symptoms and specific conditions. These procedures aim to reduce or eliminate snoring and sleep apnea by removing obstructions in the airways.
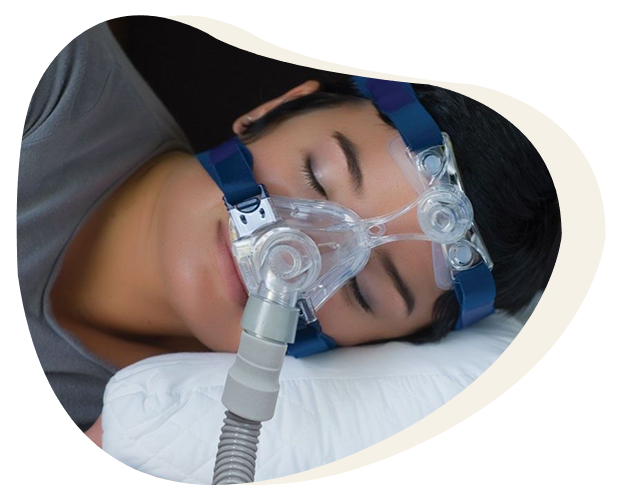
Suitable Candidates for Snoring - Sleep Apnea Surgery
Suitable candidates for snoring and sleep apnea surgery are usually individuals who experience breathing problems during sleep, have been diagnosed with sleep apnea or have breathing problems caused by anatomical problems. These surgical options usually aim to correct obstructions in the adenoid, tonsils, base of the tongue or other anatomical structures. Suitable candidates are often people who have failed to respond to or tolerate conservative treatments. However, every patient situation is different, so the assessment of suitability for sleep apnea surgery should be performed by a sleep specialist or a specialized surgeon. Surgical intervention should be individualized according to the individual’s specific condition and symptoms.
Contact Us!
Snoring - Sleep Apnea Surgery Recovery Process
The recovery process after snoring and sleep apnea surgery varies from individual to individual. Generally, surgical intervention aims to correct obstructions in the adenoid, tonsils, base of the tongue or other anatomical structures. The healing process is determined by the surgical method and the general health status of the patient. Mild pain, swelling and discomfort in the throat are normal in the first few days after surgery. Patients usually return to normal within a certain period of time and improvement in breathing problems is noticeable. However, the full recovery process varies depending on the individual’s general state of health, the complexity of the surgical intervention and the type of anatomical corrections. It is important to take medication regularly, avoid certain activities and follow post-surgical instructions to support a successful recovery. Patients should follow post-surgical check-ups regularly and contact their doctor immediately in case of any problems.

